NO Norway - Scenario Results and Monitoring Approaches
National Contact Point
| Information in Norwegian language: | National Contact Point Norway |
National Housing Stock Segments for Refurbishment
|
Download Report on National Case Study Norway |
Download EPI Tables National Case Study Norway |
Last updated: 30.05.2016
Scope
| Scale | No. of dwellings | No. of buildings | No. of inhabitants | m² reference area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| National | ~ 2.45 million | ~ 1.51 million | ~ 5.11 million | ~ 244 million (heated area) |
Description of the action
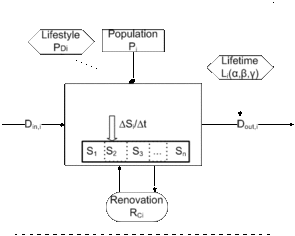
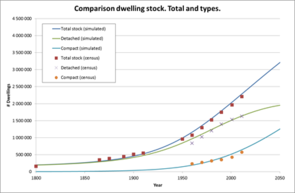
The main objective of the case study for Norway was to examine the national housing stock according to typologies developed during EPISCOPE (see Norwegian Building Typology), in order to identify the present composition and distribution of the stock in type/age segments, likely future changes in stock size and composition, and the energy and CO2 emission profiles of this stock towards 2020, 2030 and 2050.
In order to do this, a dynamic model of past and future demand for floor area, energy intensity and CO2 emission coefficients was developed and validated for the Norwegian national housing stock. The model uses the concept of dynamic MFA modelling (material flow analysis) in order to provide a mass-balance consistent quantification of annual changes in the stock, the stock change, the stock inflows (new constructions), the stock outflows (demolition) and energy refurbishment activities. This is done for each type/age segment of the housing stock, and by quantifying these results on a number of dwellings basis and a reference floor area basis. Key input variables are number of capita, capita per household, floor area per household, building lifetimes and renovation frequencies, as well as input values for annual energy intensity and CO2 emission coefficient data for each type/age segment of the building stock typology. Such input data are provided for each year between 1960 and 2015 (for historic valuation) and between 2015 and 2050 (for scenario analysis).
The advantage of such a modelling approach is better estimation of the housing stock’s long-term dynamic changes, which are highly non-linear and therefore in contrast to the linear assumptions normally assumed in building stock scenarios. Results from the stock dynamics modelling are a consequence of the identification and selection of candidate technology measures for the building envelope and energy supply system. This is carried out by using TABULA model energy balance outputs for common (synthetic average) building typology archetypes for the Norwegian national housing stock, validated by the use of energy performance indicators for Norway, and emission data for Norwegian energy-ware consumption gathered from state-of-the-art LCA methodology.
The Norwegian EPISCOPE case study provides scenario forecasts of the energy supply and CO2 emission situation for the aggregated national dwelling stock towards 2030 and 2050, and thereby compliments in a good way a previous similar (typology-based) study in Norway that only examines the likely development towards 2020. The EPISCOPE case study is linked to two PhD-student and five MSc-student research projects, supporting these students in a valuable way as well as drawing upon their competence and results. The overall results from the case study confirm that it will not be possible to meet 2030 and 2050 general policy targets regarding CO2 emission reductions, even if all dwellings in Norway are upgraded to the ambitious renovation level defined in EPISCOPE when they (statistically) are to be exposed to renovation due to ageing. Hence, other actions will be needed in addition to ambitious technology improvements.
Cooperation Partners
| Responsible for the content of this page: NTNU - Norwegian University of Science and Technology (contact information) |