- >
- Building Stock Monitoring>
- Concept of "Average Buildings"
Concept of "Average Buildings"
The determination of the monitoring indicators includes a certain effort of summarising and condensing. The EPISCOPE idea of "Average Buildings" is to take advantage of the exist-ence of the scenario indicators from national models to set up a very simple calculation scheme in parallel: The total values of all relevant input, interim and output quantities (number of apartments, floor area, envelope area, energy need for heating, final energy consumption, ...) are divided by the number of buildings counted in the building stock subgroup. So, "average buildings" are being constructed which are theoretical (synthetical) buildings with geometrical and thermo-physical characteristics equal to the average of the building stock subset which they represent. The annual energy balance for heating and DHW of average buildings are calculated in the same manner as for real buildings. Projections to the building stock can be done by multiplying the single building related figures with the total number of buildings.
The advantages of the definition and calculation of "average buildings" are:
- for the making of a model: The simplified parallel calculation enables plausibility controls of the own model.
- for the communication of results: The statements about the total building stock are more seizable, large numbers can be pictured. The datasets can also be used in conventional EPC rating software.
- for the practical relevance of the model output: The results can be used as benchmarks to compare features and energy consumptions of distinct real buildings. Projections can be easily done for other subsets of the same building stock.
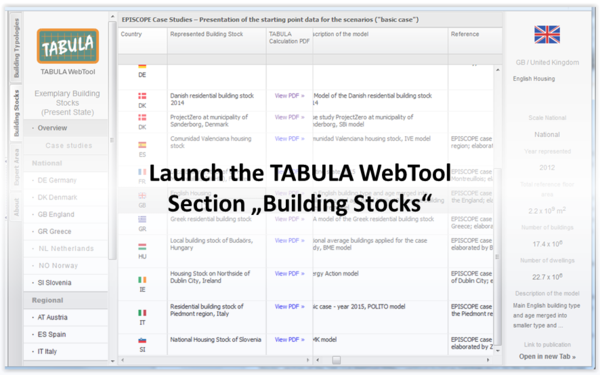
Against that background the EPISCOPE experts decided to use the average buildings concept for dissemination of parts of their results: For all case studies the basic case (existing state) was transformed to the TABULA data structure, entered in the TABULA.xlsm master file to be displayed in form of average buildings by the "Building Stocks" section of the TABULA WebTool (http://webtool.building-typology.eu/). So the documented average buildings provide a rough picture of the starting point of scenario calculations.
The WebTool section "Building Stocks" includes the following areas
- Menu item "Overview": This table displays the key values of the observed building stocks in the present state. These are the scale level, the basic data (e.g. reference areas), the calculation results from the TABULA WebTool and from the individual building stock models.
- Menu items for the case studies of the different countries, subsumed under "National", "Regional" and "Local". Here the TABULA building stock calculation can be viewed – in-cluding all input and output data. This calculation is performed using standard TABULA boundary conditions. At the end the relation of the results from the individual building stock model and from the TABULA standard calculation is determined. Under the precondition that the scenario models are validated or calibrated by real consumption values the relation separate model to simplified TABULA provides ratios for the calibration of the TABULA calculation to the typical level of measured consumption (for the given average state of the building stock subgroups).
Access to the TABULA WebTool - "Building Stocks" / "Average Buildings"
2017-07-21 15:30 +++ Error caused by power outage has been fixed.
2017-07-20 15:00 +++ NOTIFICATION +++
Disturbance of the webtool database. The error will soon be fixed ...
www.webtool.building-typology.eu
--> select section "Building Stocks"
Explanation of codes used for heat generators and energy carriers
Extract from the documentation of the TABULA method (http://episcope.eu/fileadmin/tabula/public/docs/report/TABULA_CommonCalculationMethod.pdf)
Heating system: heat generator types
|
Code_Type_SysHG |
Name_Type_SysHG |
Description_Type_SysHG |
|
code of the heat generator type (heating system) |
name of the heat generator type (heating system) |
description of the heat generator type (heating system) |
|
B |
boiler |
boiler (type unknown) |
|
B_NC |
boiler, non-condensing |
non-condensing boiler (further details unknown) |
|
B_NC_CT |
boiler, non-condensing, constant temperature |
constant temperature non-condensing boiler |
|
B_NC_LT |
boiler, non-condensing, low temperature |
low temperature non-condensing boiler |
|
B_C |
boiler, condensing |
condensing boiler |
|
B_WP |
wood-pellets boiler |
boiler for combustion of wood pellets |
|
G_IWH |
gas-fired instantaneous water heater |
instantaneous water heater, fired by gas (tankless) |
|
G_IWH_NC |
gas-fired instantaneous water heater, non-condensing |
instantaneous water heater, fired by gas (tankless) |
|
G_IWH_C |
gas-fired instantaneous water heater, condensing |
instantaneous water heater, fired by gas (tankless), condensing |
|
G_SH |
gas-fired space heater |
gas-fired space heater |
|
E |
direct electric heat generator |
direct electric, not specified: any device which uses electricity for direct heat generation, e.g. electric stoves (no heat pumps which use also heat from the environment) |
|
E_Immersion |
electric immersion heater |
electric heating rod or coil, immersed in a water storage |
|
E_Storage |
electrical night storage space heater |
electrical night storage space heater (off-peak storage heating), heat emission by convection |
|
E_UnderFloor |
electrical underfloor heating |
electrical underfloor heating |
|
E_SH |
electrical space heater |
electrical space heater: radiative heater or (forced) convection heater |
|
HP |
heat pump |
heat pump (type unknown), remark: also reversible engines that work as a cold generator in summer are to be considered here or (if heat source is known) below |
|
HP_Air |
heat pump, heat source external air |
air source heat pump: heat pump, using the external air as the heat source |
|
HP_Ground |
heat pump, heat source ground |
ground source heat pump (or geothermal heat pump): heat pump, using the ground as the heat source |
|
HP_ExhAir |
heat pump, heat source exhaust air |
heat pump, using exhaust air of a ventilation system as the heat source |
|
HP_Water |
heat pump, heat source ground water |
heat pump, using ground water or a water stream as the heat source |
|
HP_Other |
heat pump, other heat sources |
heat pump, using more than one or other heat sources (e.g. industrial exhaust heat, low-temperature district heat) |
|
Stove |
stove |
stove, fuel fired |
|
Stove_L |
stove for liquid fuels |
stove for liquid fuels, especially oil stove |
|
Stove_S |
stove for solid fuels |
stove for solid fuels, especially wood and coal |
|
OpenFire |
open fire |
open fire (fireplace, mantle) |
|
TS |
district heating transfer station |
heat exchanger (heat transfer station, heat substation) of a district heating system |
|
CHP |
combined heat and power generation |
cogeneration system: combined heat and (electric) power generation |
|
Solar |
thermal solar plant |
thermal solar plant |
|
Steam |
steam generator |
steam generator (any type) |
|
Other |
other |
other generator type |
DHW system: heat generator types
|
Code_Type_SysWG |
Name_Type_SysWG |
Description_Type_SysWG |
|
code of the heat generator type (domestic hot water system) |
name of the heat generator type (domestic hot water system) |
description of the heat generator type (domestic hot water system) |
|
B |
boiler |
boiler (type unknown) |
|
B_NC |
boiler, non-condensing |
non-condensing boiler (further details unknown) |
|
B_NC_CT |
boiler, non-condensing, constant temperature |
constant temperature non-condensing boiler |
|
B_NC_LT |
boiler, non-condensing, low temperature |
low temperature non-condensing boiler |
|
B_C |
boiler, condensing |
condensing boiler |
|
B_WP |
wood-pellets boiler |
boiler for combustion of wood pellets |
|
G_IWH |
gas-fired instantaneous water heater |
instantaneous water heater, fired by gas (tankless) |
|
G_IWH_NC |
gas-fired instantaneous water heater, non-condensing |
instantaneous water heater, fired by gas (tankless) |
|
G_IWH_C |
gas-fired instantaneous water heater, condensing |
instantaneous water heater, fired by gas (tankless), condensing |
|
G_Tank |
gas burner for directly heated DHW tank |
gas burner as a heating element of a domestic hot water tank (separately from space heating system) |
|
E |
direct electric heat generator, not specified |
direct electric, not specified: any device which uses electricity for direct heat generation, e.g. electric heating element in water storage, instantaneous water heater |
|
E_Immersion |
electric immersion heater |
electric heating rod or coil, immersed in a water storage |
|
E_IWH |
electric instantaneous water heater |
electric instantaneous water heater (tankless) |
|
HP |
heat pump |
heat pump (type unknown), remark: also reversible engines that work as a cold generator in summer are to be considered here or (if heat source is known) below |
|
HP_Air |
heat pump, heat source external air |
air source heat pump: heat pump, using the external air as the heat source |
|
HP_Ground |
heat pump, heat source ground |
ground source heat pump (or geothermal heat pump): heat pump, using the ground as the heat source |
|
HP_ExhAir |
heat pump, heat source exhaust air |
heat pump, using exhaust air of a ventilation system as the heat source |
|
HP_Water |
heat pump, heat source ground water |
heat pump, using ground water or a water stream as the heat source |
|
HP_Cellar |
heat pump, heat source: cellar air |
heat pump, using cellar air as heat source |
|
HP_Other |
heat pump, other heat sources |
heat pump, using more than one or other heat sources (e.g. industrial exhaust heat, low-temperature district heat) |
|
TS |
district heating transfer station |
heat exchanger (heat transfer station, heat substation) of a district heating system |
|
CHP |
combined heat and power generation |
cogeneration system: combined heat and (electric) power generation |
|
Solar |
thermal solar plant |
thermal solar plant |
|
Steam |
steam generator |
steam generator (any type) |
|
Other |
other |
other generator type |
Energy carriers / energywares
|
Code_EnergyCarrier |
Name_EnergyCarrier |
Description_EnergyCarrier |
|
identification of the energy carrier |
name of the energy carrier |
detailed description of the energy carrier |
|
Gas |
natural gas |
natural gas, type unknown |
|
Gas_E |
natural gas E |
natural gas E |
|
Gas_LL |
natural gas LL |
natural gas LL |
|
Gas_Liquid |
liquid gas |
liquid gas |
|
Oil |
heating oil |
heating oil |
|
Coal |
coal |
coal, type unknown |
|
Coal_Hard |
hard coal |
hard coal |
|
Coal_Lignite |
lignite coal |
lignite coal |
|
Bio |
biomass |
biomass, type unknown |
|
Bio_FW |
firewood |
firewood |
|
Bio_WP |
wood pellets |
wood pellets |
|
Bio_WC |
wood chips |
wood chips |
|
Bio_Other |
other biomass |
biomass, if different from firewood or wood pellets |
|
El |
electricity |
electricity |
|
El_OP |
off-peak electricity |
off-peak electricity |
|
El_Prod |
electricity production |
electricity production by combined heat-power generation |
|
DH |
district heating |
district heating, type unknown |
|
DH_Gas_NoCHP |
district heating gas without chp |
district heating, fuel gas, heat generation without combined heat and power (chp) |
|
DH_Gas_CHP33 |
district heating gas with 33% chp |
district heating, fuel gas, heat generation with combined heat and power (chp) fraction 33% |
|
DH_Gas_CHP67 |
district heating gas with 67% chp |
district heating, fuel gas, heat generation with combined heat and power (chp) fraction 67% |
|
DH_Gas_CHP100 |
district heating gas with 100% chp |
district heating, fuel gas, heat generation with combined heat and power (chp) fraction 100% |
|
DH_Oil_NoCHP |
district heating oil without chp |
district heating, fuel oil, heat generation without combined heat and power (chp) |
|
DH_Oil_CHP33 |
district heating oil with 33% chp |
district heating, fuel oil, heat generation with combined heat and power (chp) fraction 33% |
|
DH_Oil_CHP67 |
district heating oil with 67% chp |
district heating, fuel oil, heat generation with combined heat and power (chp) fraction 67% |
|
DH_Oil_CHP100 |
district heating oil with 100% chp |
district heating, fuel oil, heat generation with combined heat and power (chp) fraction 100% |
|
DH_Coal_NoCHP |
district heating coal without chp |
district heating, fuel coal, heat generation without combined heat and power (chp) |
|
DH_Coal_CHP33 |
district heating coal with 33% chp |
district heating, fuel coal, heat generation with combined heat and power (chp) fraction 33% |
|
DH_Coal_CHP67 |
district heating coal with 67% chp |
district heating, fuel coal, heat generation with combined heat and power (chp) fraction 67% |
|
DH_Coal_CHP100 |
district heating coal with 100% chp |
district heating, fuel coal, heat generation with combined heat and power (chp) fraction 100% |
|
DH_Bio_NoCHP |
district heating biomass without chp |
district heating, fuel biomass, heat generation without combined heat and power (chp) |
|
DH_Bio_CHP33 |
district heating biomass with 33% chp |
district heating, fuel biomass, heat generation with combined heat and power (chp) fraction 33% |
|
DH_Bio_CHP67 |
district heating biomass with 67% chp |
district heating, fuel biomass, heat generation with combined heat and power (chp) fraction 67% |
|
DH_Bio_CHP100 |
district heating biomass with 100% chp |
district heating, fuel biomass, heat generation with combined heat and power (chp) fraction 100% |
|
Other |
other |
other energy carriers |
|
- |
not existent |
not existent or no energyware (e.g. solar heat produced in the building) |